How to detect a failure
Once you have definitely confirmed that there is a failure in the master server, if you need to switch all terminals and applications to the backup (slave) server, follow this procedure.
Before initiating the recovery procedure, it is very important to assess the master server failure. There are many different possible reasons for a failure: the connection between servers, the connection with the database, the server itself, etc.
HOW TO CONFIRM IF THE FAILURE REQUIRES RECOVERY:
- First, as the slave server is continuously connected and inquiring the master server, in case of a failure, the supervisor service of the slave server will:
- Send an error mail to warn about the need of change from slave to master.
- Write in the event log of the operative system.
- If the previous has happened, or if you want to manually check, you can check the connection with the master server and its database.
NOTE: For more information, please see: Introduction Server Recovery.
1. Manual check of the MASTER connection
There are 2 ways to confirm the failure of the master server. You should perform BOTH A) and B):
A) From the terminal
Check if the connection of the master, with the server and the database, is correctly working:
- Double click on the edinn® M2 icon of your desktop or search in the Window search engine and execute “edinn M2”.
- In the Login window you will see 2 icons at the top:

- If the icon
 is red, means that connection with the server has failed. Contact your technical service to try to reconnect.
is red, means that connection with the server has failed. Contact your technical service to try to reconnect. - If the icon
 is red, means that connection with the database has failed. Then, contact your technical service to try to reconnect.
is red, means that connection with the database has failed. Then, contact your technical service to try to reconnect.
If any of icons is green, this means that the failure has not been produced because of the master server and the recovery procedure should NOT be performed. Instead, it is likely that an error in the connection between the slave server and the master server has happened.
B) From the slave server
- Run edinnM2_Console.exe as administrator in the slave server.
- Go to the Supervisor tab and, on the Recovery section, click Test to test the connection with master server.
- Press "Yes" to proceed. If any error occurs, it will appear an error message like the one that follows:
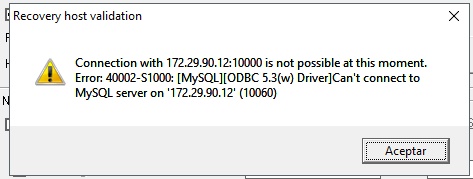
If the connection can be stablished, a success message will appear like this "Connection with HostI:Port successful!". This means that the master server is running, and the recovery procedure should NOT be performed.
If, by the previous A) AND B), you have definitely confirmed that there is a failure in the master server, if you need to switch all terminals and applications to the backup (slave) server, follow this procedure.
2. Emails and Event log
When the supervisor service of the slave server detects a failure, sends an ERROR eMAIL and writes in the EVENT LOG.
There are 3 possible types:
Some examples:
- If it is correctly working:
- Email: "Run 100% updated"
- Event log: will not show neither an error nor a warning.
- When the supervisor service is waiting to connect to the master database to obtain the status but the connection takes time:
- Email: "connecting"
- Event log: writes a connecting warning entrance.
- When there is not consistency between the master and the slave database:
- Email: "Operations error: #### Could not execute Update_rows"
- Event log: writes a warning.
- When the connection with the master timed out.
- Email: "IO error: #### reconnecting to master"
- Event log: writes an error.
